Web Hooks
Some features available in Central may not yet be implemented in New Central. We are actively developing feature parity and working to bring all capabilities to the new platform.
Web Hooks are a paid feature available to Essential and Commercial subscribers. Details about what we charge for and how to manage your subscription are available on the billing page.
For an overview of current pricing and terms including suggested use cases, please see the Pricing page on our website.
Subscribers can receive notifications of changes to their networks, network members, and organizations on my.zerotier.com via Web Hooks.
Configuring Web Hooks
Go to the Account page. Under Your Organization there is a section called Webhooks.
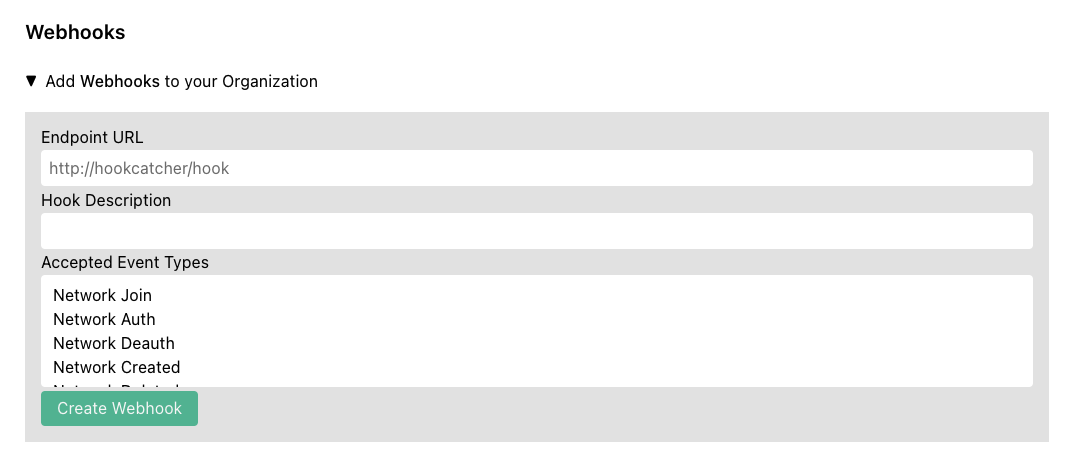
Enter the URL your HTTP(S) endpoint that will receive the webhook and (optionally) enter a description, then select the event types you wish to receive on the webhook.
See github.com/zerotier/ztchooks for example code for receiving & processing webhooks.
All hooks fired will contain the following three fields:
{
"hookd_id": ...,
"org_id": ...,
"hook_type": ...,
}
The rest of the fields vary by hook_type. Full definitions of all of the fields can be found here.
Hook Types
-
Network Join (
NETWORK_JOIN) - Fired when a new member is requesting to join a network. NOTE: This is only fired once when the network controller first receives the join request from the network member. -
Network Auth (
NETWORK_AUTH) - Fired when an administrator authorizes a new member to a network. -
Network Deauth (
NETWORK_DEAUTH) - Fired when an administrator revokes authorization from a network. -
Network Created (
NETWORK_CREATED) - Fired when an administrator creates a new network. -
Network Deleted (
NETWORK_DELETED) - Fired when an administrator deletes a network. -
Network Configuration Change (
NETWORK_CONFIG_CHANGED) - Fired when an administrator changes the configuration of a network. -
Network SSO Login (
NETWORK_SSO_LOGIN) - Fired when a user is authorized/reauthorized to a network via SSO. -
Network SSO Login Error (
NETWORK_SSO_LOGIN_ERROR) - Fired when there is an error authorizing/reauthorizing to a network via SSO. -
Member Configuration Change (
MEMBER_CONFIG_CHANGED) - Fired when an administrator makes a configuration change to a network member. -
Member Deleted (
MEMBER_DELETED) - Fired when an administrator deletes a network member. -
Organization Invite Sent (
ORG_INVITE_SENT) - Fired when the account owner invites an administrator to the network. -
Organization Invite Accepted (
ORG_INVITE_ACCEPTED) - Fired when the invitee accepts and joins the organization. -
Organization Invite Rejected (
ORG_INVITE_REJECTED) - Fired when the invitee rejects the invitation. -
Organization Member Removed (
ORG_MEMBER_REMOVED) - Fired when the account owner removes a member from the organization.
Retries
If a hook fails to be sent for any reason, it will be retried up to a maximum of 10 times with an exponential backoff policy. The 2nd attempt will be approximately 1 minute after the first. The third approximately 2 minutes after the 2nd, and so on to a maximum of 1 hour between attempts. If there is still a failure after 10 attempts, the call will be abandoned.
Web Hook Security
In order enhance security, and to prevent replay attacks, we have implemented a hook signing algorithm so you can verify each hook request as you receive it. We have also provided a Go Library and a TypeScript Library for your use in verifying incoming webhooks.
First you must create a Webhook Signing Secret from your account page.

The secret is a hexadecimal string. You will need a copy in order to verify webhooks. The signature will be placed in the HTTP header X-ZTC-Signature.
Go Example
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/zerotier/ztchooks"
)
const PSK = "<your_signing_secret>"
func hookCatcher(res http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
body, err := io.ReadAll(req.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
signature := req.Header.Get("X-ZTC-Signature")
if err := ztchooks.VerifyHookSignature(PSK, signature, body, ztchooks.DefaultTolerance); err != nil {
// signature verification failed
res.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
w.Write([]byte("500 - Signature Verification Failed"))
return
}
// Signature verification succeeded
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", hookCatcher)
http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
}
NOTE: A more complete example of verification & processing hooks can be found here.
It is possible to have multiple signing secrets. Hooks will be signed with all secrets, and the verification method provided by the ztchooks library does take this into account automatically.